Choosing the Right Pecan Tree
How to plant pecan tree – Selecting the appropriate pecan tree is paramount to a successful harvest. The choice depends on several interacting factors, including climate, soil conditions, and desired tree characteristics. Careful consideration of these factors will ensure a thriving tree that yields abundant, high-quality pecans for years to come. Think of it as choosing the right seed to cultivate a bountiful spiritual harvest – just as careful planning yields spiritual fruit, so too does careful planning yield a bountiful pecan crop.
Pecan Tree Variety Comparison
The selection of a pecan tree variety should be guided by a thorough understanding of the tree’s growth habits, nut characteristics, and disease resistance. Different varieties are suited to different climates and soil types. Consider these factors as you would consider the unique needs of different members of your faith community – each requires a unique approach to nurture their growth and potential.
| Variety | Growth Habit | Nut Size | Disease Resistance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stuart | Vigorous, upright | Large | Moderately resistant to scab |
| Pawnee | Vigorous, spreading | Medium-large | Good resistance to scab |
| Desirable | Vigorous, upright | Large | Susceptible to scab |
| Wichita | Vigorous, upright | Medium | Good resistance to scab |
Climate and Soil Considerations for Pecan Tree Selection
The climate and soil conditions of your planting location significantly influence the success of your pecan tree. Pecan trees thrive in well-drained, fertile soils with a slightly acidic pH (6.0-6.5). Just as a faithful community needs a strong foundation of shared values, so too does a pecan tree need the right soil conditions to flourish. Similarly, the climate should be considered; pecan trees require sufficient chill hours (the number of hours below 45°F during winter dormancy) to properly break dormancy in the spring.
Selecting a variety suited to your specific climate and soil conditions is essential for optimal growth and nut production. A variety that thrives in a hot, humid climate may struggle in a cold, dry climate, just as different people flourish under different circumstances.
Disease Resistance in Pecan Trees and Common Pecan Diseases
Selecting disease-resistant varieties is crucial for minimizing the risk of crop loss. Pecan scab, caused by the fungus
- Venturia effusa*, is a prevalent disease that can significantly reduce nut yield and quality. Other common diseases include pecan leaf scorch, caused by
- Xylella fastidiosa*, and root rot, caused by various soilborne pathogens. Choosing varieties with inherent resistance to these diseases is analogous to choosing strong spiritual practices to protect oneself from temptation and adversity. Just as a strong faith can provide resilience, so too can a disease-resistant pecan tree offer greater resilience against the challenges of nature. Investing in disease-resistant varieties is a proactive measure to ensure a healthy and productive orchard, reflecting the proactive nature of a thriving spiritual life.
Post-Planting Care
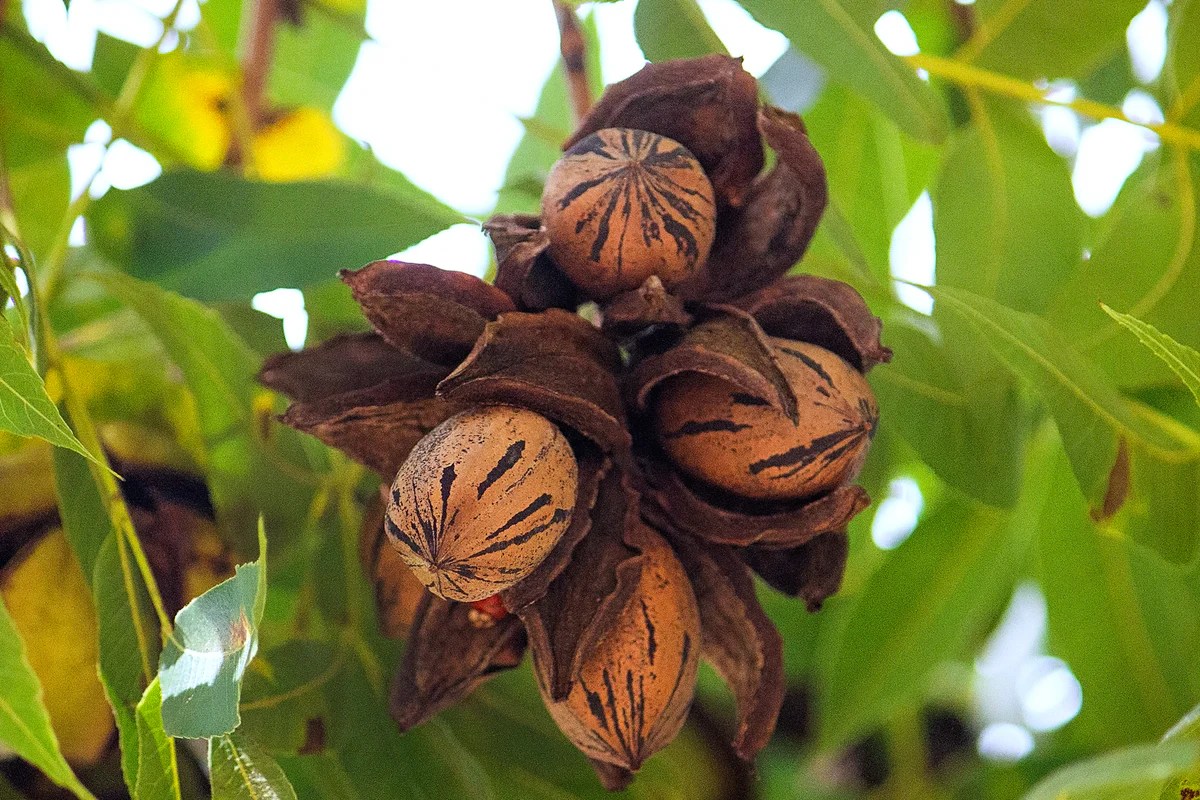

Establishing a young pecan tree requires diligent care in its initial years. Providing the right conditions for growth ensures a healthy and productive tree in the future. This involves a consistent watering schedule, proper mulching techniques, and proactive pest and disease management. Think of it as nurturing a young sapling into a strong, fruitful tree, a testament to your dedication and care.
Watering Schedule
Consistent watering is crucial, especially during the first few years. The frequency and amount will depend heavily on weather conditions, soil type, and the tree’s size. Overwatering can be as detrimental as underwatering, leading to root rot or stress. The following table provides a general guideline, but always observe the soil moisture before watering.
| Weather Condition | Watering Frequency (per week) | Watering Amount (gallons per application) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot and Dry | 2-3 times | 5-10 gallons (depending on tree size) | Deep watering is essential; water until the soil is thoroughly saturated. |
| Mild and Sunny | 1-2 times | 3-5 gallons | Monitor soil moisture; adjust watering based on dryness. |
| Cloudy and Cool | 1 time | 2-3 gallons | Less frequent watering is needed in cooler, cloudier weather. |
| Rainy | 0 times (or as needed) | N/A | Reduce or eliminate watering during periods of significant rainfall. |
Mulching
Applying mulch around the base of the young pecan tree offers several benefits. It helps retain soil moisture, reducing the frequency of watering and preventing water evaporation. It also suppresses weeds, which compete with the tree for nutrients and water. Furthermore, mulch moderates soil temperature, protecting the roots from extreme heat or cold.Mulch should be applied in a 2-3 inch layer, extending out to the drip line (the outer edge of the tree’s canopy), keeping it a few inches away from the trunk to prevent rot.
Planting pecan trees requires ample space and well-drained soil, unlike the more compact needs of citrus. If you’re interested in a smaller-scale citrus project, you might find our guide on how to plant lemon tree in pot helpful. Returning to pecans, proper watering and fertilization are key to a healthy, productive tree.
Organic mulches like wood chips, shredded bark, or composted leaves are ideal choices. Avoid using plastic mulch, which can trap moisture and lead to fungal diseases.
Pest and Disease Management
Pecan trees are susceptible to various pests and diseases. Proactive measures are essential to prevent infestations and infections. Regular inspection is key; early detection allows for timely intervention. Look for signs of insect damage, such as leaf discoloration, holes, or webbing. Check for signs of fungal diseases like leaf spots or cankers.Preventative measures include maintaining good tree health through proper watering, fertilization, and pruning.
Choosing disease-resistant varieties can significantly reduce the risk of infection. In cases of infestation or infection, consult with a local arborist or extension agent for advice on appropriate treatments. Remember, prevention is often cheaper and more effective than cure. This is a stewardship of creation, reflecting God’s care for His earth.
Ongoing Pecan Tree Maintenance: How To Plant Pecan Tree
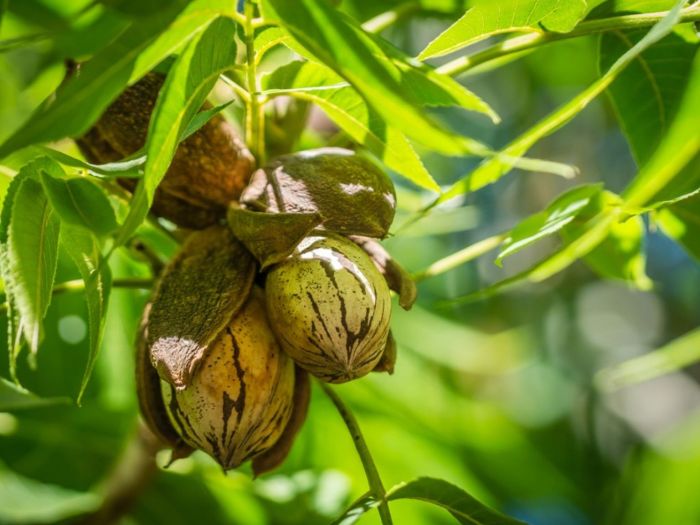

Maintaining the health and productivity of your pecan tree is a journey, much like tending to a precious vineyard. It requires consistent care and attention, mirroring the unwavering devotion we should offer to our faith. Just as diligent prayer nurtures our spiritual growth, proper maintenance ensures a bountiful harvest from your tree. This section details the essential practices to ensure your pecan tree thrives for years to come.
Pecan Tree Pruning Techniques, How to plant pecan tree
Pruning is a crucial aspect of pecan tree care, akin to shaping a young sapling’s faith into a strong and fruitful tree. Proper pruning promotes strong structural growth, maximizes sunlight penetration, and facilitates easier harvesting. The approach varies depending on the tree’s age and growth stage.
- Young Trees (0-5 years): Focus on establishing a strong central leader and scaffold branches. Remove competing leaders, crossing branches, and branches growing inward. This foundational pruning helps build a strong framework, just as we build a strong foundation in our faith through prayer and scripture. Think of it as guiding the tree’s growth towards its potential, much like guiding a child’s development.
- Mature Trees (5+ years): Pruning mature trees involves removing dead, diseased, or damaged branches, as well as branches that are interfering with each other. This helps maintain air circulation and sunlight penetration, essential for optimal nut production. It’s a process of refinement, similar to the continuous refinement of our faith through experience and reflection.
- Renewal Pruning (Older Trees): For older trees showing signs of decline, renewal pruning may be necessary. This involves removing a portion of the older wood to stimulate new growth, rejuvenating the tree’s vitality. This mirrors the spiritual renewal we experience through repentance and recommitment to our faith.
Pecan Tree Fertilization Plan
Proper fertilization is vital for the health and productivity of your pecan tree. It’s like providing nourishment to sustain spiritual growth; without proper sustenance, the tree, like our faith, can falter. A balanced fertilization program should address the tree’s nutritional needs throughout its lifespan.
A soil test is crucial to determine the specific nutrient deficiencies present in your soil. This test will guide you in selecting the appropriate fertilizer blend. Based on the results, you can select a fertilizer containing the necessary nutrients – often a blend of nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K), mirroring the three theological virtues of faith, hope, and charity that sustain our spiritual lives.
Generally, pecan trees benefit from a slow-release fertilizer applied in early spring before new growth begins. Application methods include broadcasting around the tree’s drip line or using a fertilizer injector. Always follow the fertilizer manufacturer’s instructions regarding application rates to avoid over-fertilization, which can damage the tree. Over-fertilizing is like spiritual excess – too much can be detrimental.
Pests and Diseases Management
Regular inspection for pests and diseases is essential for maintaining a healthy pecan tree. Early detection and intervention are crucial to prevent significant damage, much like addressing spiritual struggles promptly is vital to maintain our faith.
Common pecan pests include pecan weevil, aphids, and scale insects. Diseases such as scab, leaf spot, and fungal diseases can also impact the tree’s health. Regular visual inspections should be conducted to identify any signs of infestation or disease. Appropriate control measures may include cultural practices (such as proper sanitation and pruning), biological control (introducing beneficial insects), or chemical control (applying approved pesticides).
Always carefully follow pesticide label instructions and choose environmentally friendly options whenever possible. Remember, just as we should seek to live in harmony with nature, we should strive to use responsible and sustainable pest control methods.
Detailed FAQs
How long does it take for a pecan tree to produce nuts?
It typically takes 6-10 years for a pecan tree to start producing a significant nut crop, although some varieties may take longer.
How far apart should I plant pecan trees?
Spacing depends on the variety, but generally, pecan trees should be planted 30-40 feet apart to allow for adequate growth and sunlight.
Can I plant a pecan tree from a pecan nut?
While possible, it’s not recommended. Grafting or purchasing a nursery-grown tree is more reliable for ensuring the desired variety and faster fruiting.
What are the signs of a pecan tree with nutrient deficiencies?
Signs can include yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and reduced nut production. Soil testing can help determine specific deficiencies.